- Posted: 13 March 2023
You may not notice early signs of diabetes. The picture lists the most common signs to watch for. If you notice these or other signs, speak to your healthcare team.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 13 March 2023
You may have diabetes and don’t know it. Finding out that you have diabetes early helps prevent diabetes problems. There are some tests that your healthcare team may do to see if you have diabetes or are at a higher risk.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 13 March 2023
Get to know diabetes, how it affects your body, and how type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) differ. This will help you manage diabetes so that you get your blood glucose to goal.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 18 April 2023
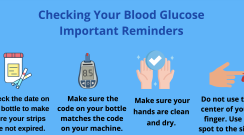
Checking your blood glucose is an important tool in managing your diabetes and preventing complications. Here are tips to keep in mind when self-testing.
Topics: Monitoring Your Blood Glucose
- Posted: 25 April 2023
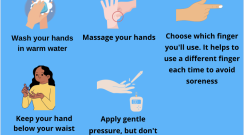
Using a glucose meter helps you understand what increases or decreases your glucose numbers such as different foods, medication, exercise, etc. Here are useful tips to keep handy when collecting a blood sample for your meter.
Topics: Monitoring Your Blood Glucose
- Posted: 26 April 2023
Managing your diabetes means that you may need to check your blood glucose at different times depending on life changes. Here the most common reasons to check your blood glucose more often than usual.
Topics: Monitoring Your Blood Glucose
- Posted: 28 April 2023
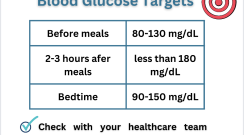
General blood glucose targets as a reference. Always check with your healthcare team as your target numbers may differ.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 24 March 2022
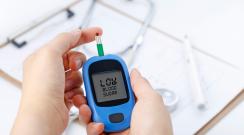
Hypoglycemia or low blood glucose is when blood glucose (sugar) drops below 70 mg/dL. How you feel when you are low may vary. Watch for these common ones.
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 14 March 2022
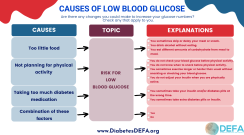
5 things that may lead to Low Blood Glucose (Sugar) or Hypoglycemia (Graphic).
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 24 March 2022
The ‘15-15 Rule’ is a way to treat low blood glucose (sugar) or hypoglycemia. It means take 15 grams of a fast carb such as half a glass of juice, wait 15 minutes, then check blood glucose again to see if it is above 70 mg/dL.
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 24 April 2023
If you are living with type 2 diabetes, here are important tips to keep handy to ensure your diabetes medication is most effective.
Topics: Medications
- Posted: 02 May 2023
Blood glucose levels can also be affected by the stress and emotions you experience.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 11 May 2023
Managing stress and your diabetes can feel overwhelming. Stress can increase your blood glucose levels, which increases your risk for complications. Here are some suggestions to taking control of your stress.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 11 May 2023
Common signs that your stress is affecting your diabetes control could be forgetting to take your medication on time or at all, and overeating or not eating enough.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 16 May 2023
Knowing about type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) and how they differ helps people at risk for diabetes and their healthcare team know when and how to check for diabetes, understand how to manage it, stay healthy and lower the risk of diabetes problems.
- Posted: 16 May 2023
There are many factors that may alter your overall mood while managing your diabetes. Here are a few suggestions on things you can do to improve your mood.
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Planning to travel this holiday season? Here are some tips and suggestions for how to travel safely and enjoy a stress-free trip.
Topics: Diabetes and Travel
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Packing for a trip? Packing your bags takes a small amount of extra preparation to enjoy a fun and safe trip. Use this helpful list to make sure you have all the essential items you need throughout your trip.
Topics: Diabetes and Travel
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Do Some Prep Work!
It’s easy to give in to temptation when you’re dining with friends. Before you go, look up the restaurant’s menu online, and choose a dish that fits with your diabetes meal plan. You also can call ahead of time to ask questions and make requests. Some chefs will prepare a special meal.
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Having diabetes shouldn’t stop you from enjoying dining out at a restaurant. The important thing is to keep an eye on your blood sugar and how it’s being affected. Check out our information on what to bring when dining out when taking insulin.
Topics: Dining Out When Taking Insulin
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Making wise and healthy food choices will help you manage your blood glucose levels and lose weight if needed. A best choice is a food that is better for you than other foods in the same group. Best choices are lower in saturated fat, trans fat, added sugar and sodium than similar foods.
Topics: Dining Out When Taking Insulin
- Posted: 06 September 2023
It's all about pushing limits, setting new goals, and becoming the best version of ourselves! Gym essentials packed and ready to go! Here’s a list of your gym bag must-haves.
Topics: Diabetes and Physical Activity
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Planning an escape to the beach? You don’t want anything to get in the way of a day enjoying the sand and sun. To make sure you have a perfect beach getaway, here’s a closer look at some things to do and items to bring that will help you have the best experience while managing your diabetes.
Topics: Diabetes and Travel
- Posted: 06 September 2023
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing complications in their feet due to poor blood circulation and nerve damage. These issues can lead to serious infections, ulcers and other foot problems if not properly cared for.
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Early detection and proper care are key in avoiding complications. If you notice any concerning symptoms, don't hesitate to consult your healthcare provider. Stay safe and take care of your feet.
- Posted: 26 June 2023
Managing diabetes during the summer months requires some additional considerations due to the potential impact of heat, increased physical activity, and changes in routine. Here are some tips to help you manage your diabetes effectively during this season.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 01 June 2023
When you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and are planning to become pregnant, your health care team will ask you to begin to lower your glucose (sugar) levels. The goal is an A1C of less than 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) by the time you become pregnant. High blood glucose (sugar) levels once pregnant can harm you and your baby. Pregnant women with diabetes have lower blood glucose (sugar) goals than women who are not pregnant.
Topics: Pregnancy
- Posted: 23 May 2023
The plate method is a simple and practical way to plan balanced meals for individuals with diabetes. It helps ensure that your meals contain a variety of nutrients and are portioned appropriately.
Topics: Diabetes and Nutrition
- Posted: 01 June 2023
Physical activity can have an impact on blood glucose levels, and it is important to take steps to prevent low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) when engaging in physical activity. Here are some strategies to help prevent low blood glucose during physical activity.
Topics: Diabetes and Physical Activity
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Physical activity and healthy snacking play crucial roles in managing diabetes.
Topics: Diabetes and Physical Activity
- Posted: 06 September 2023
Insulin loses some effectiveness when exposed to extreme temperatures. The longer the exposure to extreme temperatures, the less effective the insulin becomes. This can result in loss of blood glucose control over time. Keep insulin away from direct heat and out of direct sunlight. Follow these tips to ensure effective insulin storage.
Topics: Insulin and Other Injectables
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes, most commonly associated with type 1 diabetes. It occurs when there is a severe shortage of insulin in the body, leading to a buildup of ketones (acidic byproducts of fat breakdown) in the blood.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Ketones are chemical compounds produced by the liver when there is a shortage of insulin or when the body cannot effectively use glucose as an energy source. They are byproducts of the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Checking your blood glucose levels regularly is a crucial component of lowering your A1C and effectively managing diabetes. Remember to discuss your blood glucose testing schedule and target ranges with your healthcare team. They can provide personalized guidance and help you interpret the results to make appropriate adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Lowering your A1C (a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months) is an important goal in diabetes management. In addition to lifestyle modifications, medications may be prescribed to help achieve and maintain target A1C levels.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Creating a healthy meal plan is an essential component of lowering your A1C and managing diabetes. Here are some tips to help you develop a balanced and diabetes-friendly meal plan.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 31 May 2023
Diabetes treatment includes lifestyle changes such as healthy meals and more activity, taking medicine, and, in some cases, insulin treatment. Treatment plans will depend on the type of diabetes you have, your lifestyle, and ideas from your healthcare team. This quick guide provides some common ways to manage diabetes.
Topics: Diabetes Management
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Know if you have signs of low blood glucose (sugar) or hypoglycemia.
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Low blood glucose (sugar) or hypoglycemia, happens when you take more diabetes medicine than you need, don’t eat enough food or are more active than usual. Talk to your healthcare team about how you can prevent low blood glucose.
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose (sugar), can happen when you have diabetes. Learn some causes of high blood glucose and ways you can lower your risk.
Topics: Hyperglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
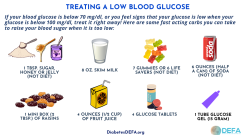
When you have low blood glucose (sugar) or hypoglycemia, eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbs to raise your blood glucose (sugar) to above 70 mg/dL. Here are some 15-gram fast acting carbs ideas you can try.
Topics: Hypoglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
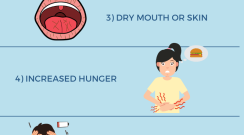
Signs that you have hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose (sugar) depend on how high your blood glucose is and how long it has been high. Learn the signs to look for so that you can take action.
Topics: Hyperglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Hyperglycemia or high blood glucose (sugar), even for a short time, can cause health problems if you don’t treat it. Here is why you should treat high blood glucose right away.
Topics: Hyperglycemia
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Hyperglycemia or high blood glucose (sugar) can cause health problems if you don’t lower your glucose. Here are some of the problems you can have if you don’t treat high blood glucose and reach your glucose goals.
Topics: Hyperglycemia