Explore the various types of diabetes, common symptoms to watch for, and how to recognize and manage hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Learn about preventive measures to reduce your risk of developing diabetes, as well as potential complications associated with the condition. Dive into the latest statistics and numbers to better understand the prevalence and impact of diabetes worldwide.
- Posted: 13 March 2024
Some signs of diabetes are being tired, thirsty, hungry, peeing a lot, losing weight without trying, seeing blurry, having sores that heal slowly, and tingling in the hands or feet. See your healthcare team if you have any of these signs. Taking care of diabetes will help you get healthy and lower your risk of problems.
- Posted: 13 March 2024
Prediabetes is when your blood glucose (sugar) is high, but not high enough to be diabetes. Learn how to lower your blood glucose and slow down the chance of having diabetes. Pre-diabetes is when the insulin you make is not working well. Your healthcare team can teach you how to plan your meals, be more active and lose some weight to lower your risk of diabetes.
- Posted: 02 June 2023
There are several misconceptions surrounding diabetes. Educating individuals about the accurate causes, symptoms, and management of diabetes can help dispel these myths and promote better understanding and support for those living with the condition.
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Low blood glucose (sugar), or hypoglycemia means your blood glucose is below 70 mg/dL. Risk of low blood sugar is higher in people with diabetes who take insulin or certain pills that may cause low blood glucose if your dose is too high, or you eat less or are more active than usual. Hypoglycemia is more severe when your blood glucose is below 54 mg/dL and can lead to passing out or having a seizure. If you are not able to help yourself, ask for help or call 911 right away.
- Posted: 02 June 2023
Hyperglycemia or high blood glucose (sugar) means your blood glucose is over 180 mg/dl (10.0 mmol/L). Risk of high blood glucose goes up if you take too little diabetes medicine, eat more than usual or are less active. If your body does not make enough insulin or is not able to use the insulin you make well, too much glucose stays in your blood. Talk to your healthcare team about how you can lower and prevent high glucose.
- Posted: 01 June 2023
Being pregnant along with living with diabetes can be hard to care for at the same time. To keep both the mother and baby healthy, close follow up is needed. It is key for pregnant women with diabetes to get special care and follow their care plan to get to and keep their blood glucose (sugar) at goal to prevent diabetes problems.
- Posted: 13 March 2024
Diabetes prevention involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use. Additionally, regular medical check-ups to monitor blood glucose levels and assess risk factors are essential. By making these lifestyle changes and managing risk factors effectively, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Posted: 01 June 2023
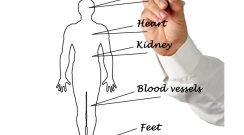
Diabetes complications can affect various organs and systems in the body, including the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and blood vessels. Common complications include cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, foot ulcers, and increased risk of infections. Proper management of diabetes through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups is crucial in preventing or delaying these complications.